What is the best protein for kids and how much do they need to consume?

Protein is recommended for children as a means to avoid nutritional deficiencies and promote proper growth and development. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) developed a table with protein requirements according to age.
How much protein do kids need?
Protein recommendations differ based on the child’s age. Current protein requirements for children are based on FAO recommendation published in 2007, as listed below. It is similar to RDAs from most countries and were derived by using a factorial calculation in which the mean requirement was maintenance needs plus an additional component for growth, which was estimated from the rate of protein deposition and efficiency of protein use.
Boys require 20% more protein than girls based on their height and weight. Children aged 5 months to 3 years should consume between 10.2 and 14 grams daily. Between 4 and 6 years, the amount increases to 18.6 grams per day. FAO recommends up to 28 grams per day for children ages 7 to 10, and 46 grams for children 11-14 years of age.
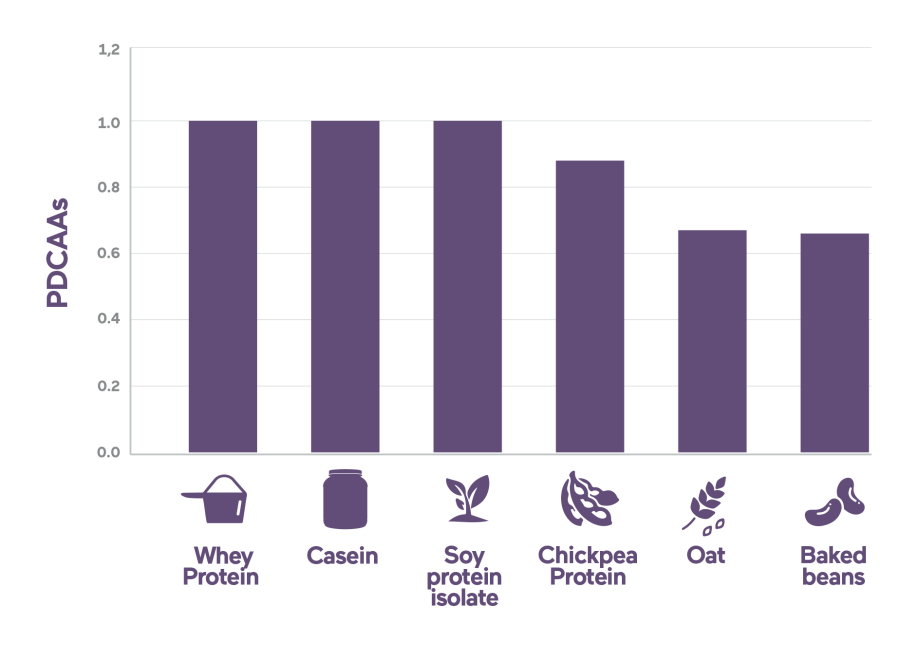
What type of protein is the best?
Not all proteins are equal. Protein quality is evaluated by Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS). It compares the amount of the essential amino acids in protein to a scoring pattern based on the essential amino acid requirements of a 2- to a 5-year-old child and its digestibility. This score PDCAAS plays essential role to assess available protein from diets and its adequacy compared to the recommendation daily intake (see below). The highest PDCAAS value that any protein can achieve is 1.0, indicating that the protein will provide 100% (or more) of all the amino acids required in the diet. Generally, casein, whey, soy, and egg are considered good quality proteins and have PDCAAS scores of 1.0, while those of tree nuts are a bit under 0.50 and wheat gluten even lower.
Overall, whey protein is a high-quality complete protein source that can meet children’s amino acid needs and nutrition requirements.
If this content was useful to you, please share it on your networks.
Reference:
Joint, W. H. O. “Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition.” World health organization technical report series 935 (2007): 1.

